From inside (document excerpt):
Rotary Mower Basics PART NO. 09167SL This page is intentionally blank. Rotary Mowers Table of Contents 1 Historical Background 2 Theory of Operation . 4 Cutting Action 6 Equipment Application . 8 Importance of the Operator . 10 Productive Equipment Operation . 11 Cutting Unit Adjustments . 15 Inspection Maintenance and Repairs 16 Rotary Blade Inspection and Sharpening 20 Toro University Technical Training 2 Rotary Mowers Historical Background The first practical concept of a rotary type mower goes back to the 1930’s.
Lawn Mowing User Manual Free Download. Power Lawn Mower Free Instruction Manual Download PDF.
The concept evolved from the need for a grass maintenance tool that could cut long grass acceptably without the cost and sophistication of a reel mower. During the 1940’s improvements in engines and material brought about increased use of rotaries but it wasn’t until after World War II that their use became a common sight. During the 1960’s the bagging concept evolved and rotary designs incorporated multi- blade configurations useful for cutting large commercial type areas. Toro University Technical Training Rotary Mowers 3 Improvements in engines and drive systems have resulted in the very effective commercial type rotary mowers that are presently available. Toro University Technical Training 4 Rotary Mowers Theory of Operation Blade mounting and drive system Blade Deck housing There are three basic structural members to a rotary cutting unit. Cutter Deck Housing The deck housing supports the blade hubs with their drive mechanism and is shaped to carry the cut grass clippings away from the deck in an effective manner. Blade mounting and drive system The blade is normally driven directly by the engine crankshaft, a hydraulic motor or through a belt pulley system to each blade hub. The blade The blade has a sharpened cutting edge at each end with a curved up sail area to create an air flow. This air flow will whip the grass blades exposing them to the blade cutting edge. The air flow also assists in carrying the cut grass blades out the discharge. Toro University Technical Training Rotary Mowers 5 Power transfer from the engine to the blades is typically done by way of belts and transfer shafts. Belt drives typically transfer a high percentage of the available horsepower to the blade and generally produce much less noise than hydraulic drive systems. Blade spindle assembly Large Diameter Ductile Cast Iron Spindle Support Ductile cast iron, stronger than aluminum or regular cast iron Solid Cold Finished Steel Spindle Shaft Large diameter shaft is resistant to torsion and bending failure Timken® Tapered Roller Bearings Support spindle shaft better than ball bearings 50% more load carrying capacity than ball bearings Blade Retainer & Anti-Scalp Cup Eliminates blade slippage and protects turf from damage The deck spindles usually run at approximately 2000 to 2500 RPM. They feature tapered roller bearing for impact resistance and durability. The bearings can be greased, and if done properly can ensure long life while also purging contaminates from the assembly.
Wikipedia’s page for Toro Company
Company Web Site: www.toro.com


 Toro Owners Manual - 1 of 28
Toro Owners Manual - 1 of 28 Toro Owners Manual - 2 of 28
Toro Owners Manual - 2 of 28 Toro Owners Manual - 3 of 28
Toro Owners Manual - 3 of 28 Toro Owners Manual - 4 of 28
Toro Owners Manual - 4 of 28 Toro Owners Manual - 5 of 28
Toro Owners Manual - 5 of 28 Toro Owners Manual - 6 of 28
Toro Owners Manual - 6 of 28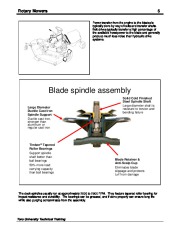 Toro Owners Manual - 7 of 28
Toro Owners Manual - 7 of 28 Toro Owners Manual - 8 of 28
Toro Owners Manual - 8 of 28 Toro Owners Manual - 9 of 28
Toro Owners Manual - 9 of 28 Toro Owners Manual - 10 of 28
Toro Owners Manual - 10 of 28